Internet Down? Follow This Essential 6-Step Guide to Fix It Fast
The internet is something we rely on without a second thought—until, suddenly, it’s gone.
Please note: This is a beginner’s guide and includes only the most common fixes for connectivity issues. It’s not a comprehensive guide with all possible troubleshooting steps.
Imagine you’re in the middle of an important task, or maybe you’re just about to reach a new level in a game, when—bam!—your internet connection drops. Suddenly, everything grinds to a halt. Frustrating, right? Losing your internet can feel like being cut off from the world, but before panic sets in, there are a few quick steps you can try to get back online.
Make Sure Your Connection Is Really Down
- Open the Command Prompt. There are multiple ways to do this, but today we’ll stick with the most common: type ‘CMD’ in the search bar and open Command Prompt. Once it’s open, type the command ‘
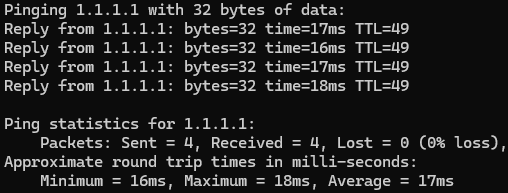
ping 1.1.1.1‘ (you can also try 8.8.8.8) and press Enter.
Pinging 1.1.1.1 replies with time as shown. If you see a response with ‘time=’ values like this, it means your internet connection is active. That’s good news—your internet isn’t down!
The issue is most likely DNS. If you see a response like ‘Request timed out.‘ or ‘Destination host unreachable.‘, there may be a different issue. Try accessing the internet on your mobile device. If it doesn’t work there either (unless using 4G), go to the next step.
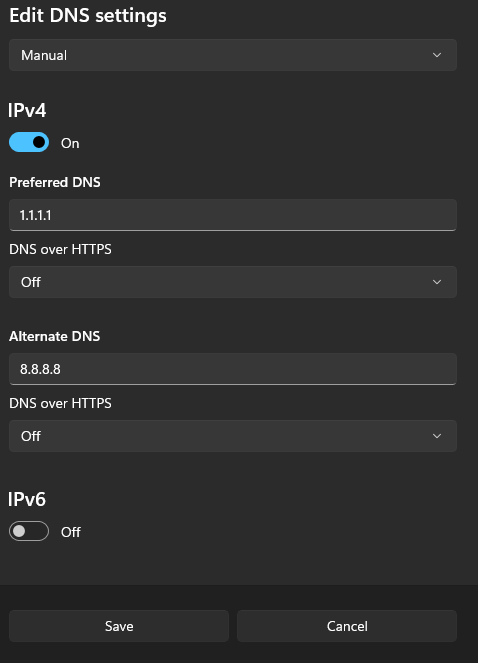
- To fix DNS, you can change the settings on your device temporarily. In Windows, enter your network settings -> right click the Windows icon -> click ‘Settings‘ -> click ‘Network & Internet‘ -> If you use ‘Ethernet‘ click this, otherwise go to ‘Wi-Fi‘.
- In here, you’ll see ‘DNS server assignment‘ -> click ‘Edit‘ -> click the dropdown menu and click ‘Manual‘ -> tick ‘IPv4‘ -> Preferred: ‘1.1.1.1‘ – Alternative: ‘8.8.8.8‘ -> Do not tick anything else -> Press ‘Save’

Change your DNS Settings like this. - For Mac OS, follow this guide.
- Now you can try browsing the internet again. Does it work? If yes, good! All set! If not, let’s continue troubleshooting.
Verify Your IP Address and Router Connection
If DNS wasn’t the issue, check if your PC has an IP address.
Open up your Command Prompt:
- Search for ‘cmd‘ in Windows
- Open ‘Command Promp‘
- Write ‘
ipconfig‘ - Look for IPv4 Address.
If this shows any of these addresses: 10.xxx.xxx.xxx, 192.168.xxx.xxx, 172.16.xxx.xxx (xxx means random numbers) – then you have an IP address. Next, try pinging your ‘Default Gateway‘. - To do this, type ‘ping‘ and after, type the address that you have.
- If it responds like the ping image above, then good. You can reach your router. This tells us that the cabling is good and your device has a working network card.
- If you got a 169.254.xxx.xxx address, your computer is not getting an IP address from your router. Try getting a new IP adress manually.
- To get a new address, type the command: ‘
ipconfig /renew‘ - If you see a error message such as ‘An error occurred while renewing interface [interfacename]: Unable to contact your DHCP server. Request has timed out.‘, then reboot your router and then attempt the command again.
Check your router and cabling
Before diving into further troubleshooting, take a look at your router’s indicator lights. Red lights usually signal a problem, while orange and green lights are generally fine. Orange often means a 1Gbps connection, and green typically indicates 100Mbps.
If you notice a red light on any of the following: ‘WAN‘, ‘Optical‘, ‘DSL‘, ‘Internet‘, or ‘Broadband‘ indicators (or a red globe icon), this could point to an issue with your ISP. If there’s no light at all on this indicator, make sure all cables are securely connected.
Try swapping out faulty cables; If you have a spare Ethernet cable it to rule out a faulty cable. To remove a cable, press the ‘notch’ on the plug and gently pull it out.
Additional check:
Some fiber connections have a modem before your router. If you have one, which is most likely close to your router, check if this also has power and is connected.
Next, try rebooting all network devices—routers, access points, and so on. Wait 30 seconds before plugging the power back in. You’d be surprised how often a simple reboot fixes everything.
If the light still doesn’t turn green, you may need to contact your ISP, as the issue could be on their end.
If your router has no lights at all, the problem might be a tripped breaker. Check your circuit breaker to ensure the router has power. If there’s power at the outlet but your router remains off, ensure the power cord is securely connected and check if the router has a power button. If it’s switched on but still unresponsive, the router may be faulty.
Network works on mobile devices, but not on computer
If your mobile devices have internet access but your computer does not, you may need to update your network drivers.
If you’re using Wi-Fi, try connecting your computer directly to the router with an Ethernet cable. If this gives you internet access, proceed to update your drivers.
To update your drivers:
- Visit your computer manufacturer’s website (e.g., ASUS, Dell, HP) and look for the driver support section.
- Search for your model by entering the serial number or service tag, often found on the bottom or back of your device.
- Download and install the latest drivers for your network adapter.
Additionally, run Windows Update to ensure your operating system is fully up-to-date.
Check cables and connections
Check that all cables are fully inserted. Ethernet cables typically make a ‘click’ sound when properly connected. Inspect your cables for any visible damage—replace any that show wear. If you’re using flat cables, be aware that cheaper versions tend to be unreliable and may break over time.
If you have multiple cables connected to your router, check if the indicator lights are on. For example, if your computer is connected to ‘LAN1‘ and the light isn’t lit, it could indicate a cabling, hardware, or driver issue. Try connecting it to ‘LAN2‘; if it works, the port on your router might be faulty.
Wi-Fi and airplane mode
If you’re using Wi-Fi, check if airplane mode is enabled by clicking the Network icon at the bottom right of your screen. Make sure airplane mode is off.
Is the Wi-Fi icon blue or grey in this menu? Blue means it’s on and should show available Wi-Fi networks; grey means it’s off, so click it to turn it on.
In the list, does it say ‘Connected‘ next to your network? If not, try reconnecting to your Wi-Fi network. If prompted, enter your Wi-Fi password. If it still doesn’t work, you may need to “forget” the network and then re-enter your password.
Is your wireless network in range and has good signal? If yes, good. If not, you need to move closer to your router.
If your computer shows a strong Wi-Fi signal but still isn’t connecting, try rebooting your PC first. If that doesn’t work, reboot your router and check the connection again.
More Troubleshooting Tips for Limited or No Internet Access
Check your VPN
If you are using a VPN (e.g. NordVPN, WindScribe, PIA) ensure that its ‘internet kill switch’ is set to ‘Off’ when the VPN is disconnected. The internet kill switch prevents internet access when the VPN is off, which is a safety feature designed to protect privacy—an important aspect of everyday life for many.
Some VPNs, like Windscribe, use other terms such as “Firewall.” Check if this is set to “Always On.” If it is, your internet connection will be unavailable until the VPN is active.
Paid Your Bills Lately?
This might seem like a “du-uh” moment, but I’ll say it anyway—have you paid your ISP bill?
Unpaid bills will, unsurprisingly, cut off your internet connection.
Try another web browser
If you have a different web browser installed on your computer, try using it. If you don’t have another browser, try opening the website in incognito mode.
If the website works in the other browser or incognito mode, the issue is likely related to your browser’s CACHE. Clear your browser cache and try again.
Check your computer’s time and date settings
If you are encountering SSL errors or struggling to access many websites, check your computer’s time and date settings. Incorrect settings can cause issues, as SSL certificates rely on your system’s accurate time and date. Some websites may fail to load or display certificate warning messages.
It cannot be stressed enough: never enter sensitive information on a website without HTTPS or a valid SSL/TLS certificate. Information sent to websites without encryption can be intercepted and read in plain text, putting your data at serious risk.
Check for Service Outages
Contact your internet service provider or check their website to see if there’s a known outage in your area. Sometimes, the issue is out of your hands.
Try using your mobile as a hotspot
Set up your mobile as a hotspot and connect your computer to it. If your computer connects successfully, then the issue is likely with your network and not your device.
Run a Built-In Troubleshooter
Most operating systems have built-in network troubleshooters. Run the troubleshooter to detect and resolve common issues automatically.
- On Windows: Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status and select Network troubleshooter.
- On MacOS: Open System Preferences > Network, and use the Assist Me option.
Article summary
To summarize, start by checking your device’s connection status and reboot if necessary. Verify your IP address and DNS settings, check your router’s indicator lights, and try basic fixes like reconnecting or resetting your network settings.
If all else fails, contact your ISP for further assistance.
When to Contact Tech Support
If none of these steps work and your connection issues persist, it might be time to contact your ISP or a tech support professional. They can help troubleshoot issues that go beyond basic connectivity fixes.
Tips for Further Learning
Want to learn more? Understanding basic networking terms like DNS, IP addresses, and gateways can make troubleshooting easier next time. Consider reading beginner guides on networking to deepen your knowledge.
You can explore this in the “Start Here” section on Nuvorix!